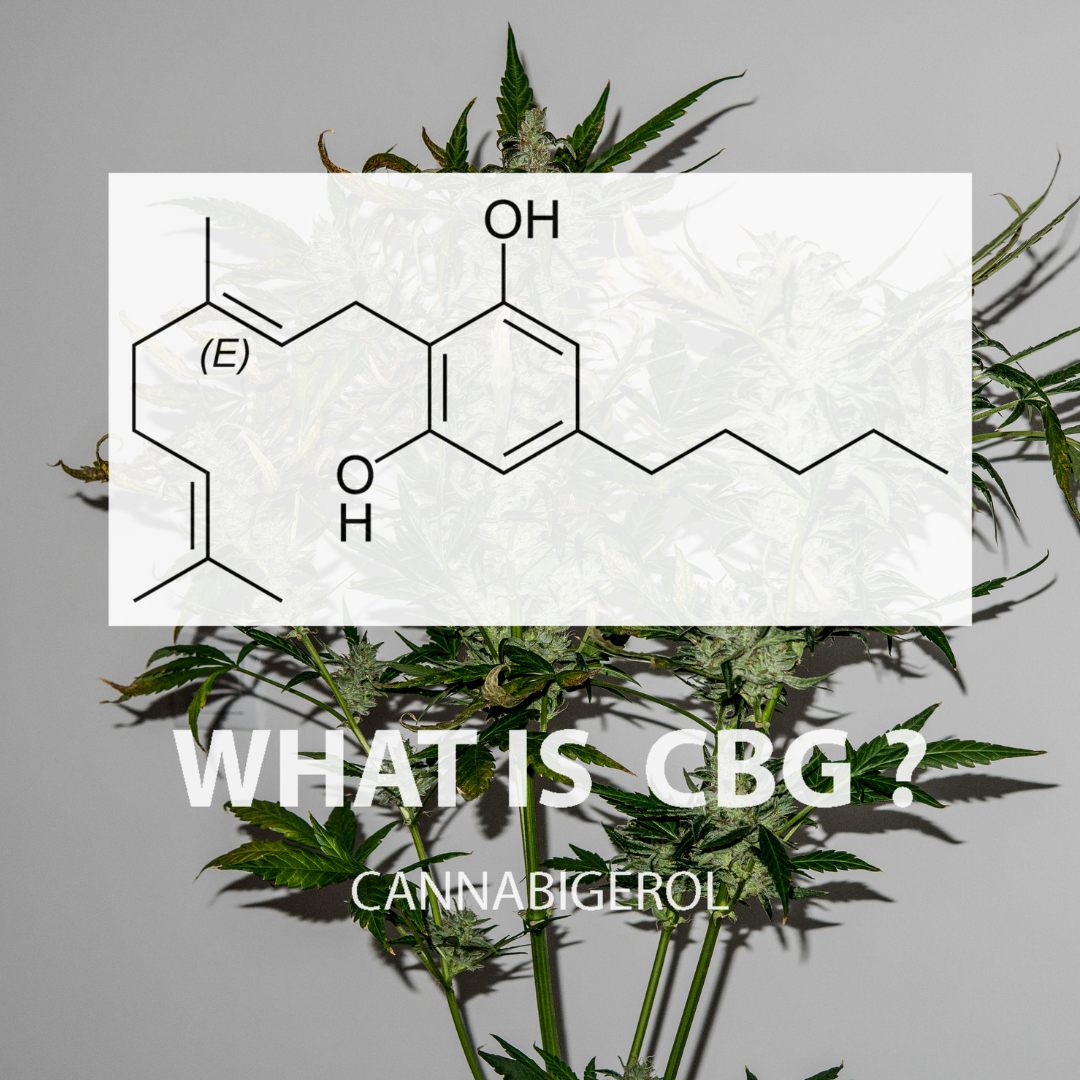
Cannabigerol, or CBG, is garnering increasing attention in the realm of cannabis research and wellness communities alike. Often referred to as the “mother cannabinoid,” CBG serves as a precursor to other cannabinoids such as CBD (cannabidiol) and THC (tetrahydrocannabinol). Despite being less abundant than its counterparts in most cannabis strains, CBG’s potential therapeutic properties are captivating scientists and enthusiasts alike.
CBG is produced through the enzymatic transformation of cannabigerolic acid (CBGA), the acidic form of CBG. As the cannabis plant matures, CBGA undergoes decarboxylation, resulting in the formation of CBG, CBD, THC, and other cannabinoids. Due to this process, younger cannabis plants contain higher concentrations of CBG, while more mature plants tend to have higher levels of CBD and THC. One of the most intriguing aspects of CBG is its potential therapeutic applications. While research is still in its nascent stages, preliminary studies suggest that CBG may possess various pharmacological properties, including anti-inflammatory, neuroprotective, and antibacterial effects. Additionally, CBG shows promise in alleviating symptoms associated with conditions such as glaucoma, inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), and neurodegenerative disorders.
CBG’s interaction with the endocannabinoid system (ECS) plays a crucial role in its therapeutic effects. Like other cannabinoids, CBG interacts with cannabinoid receptors within the ECS, particularly CB1 and CB2 receptors, albeit with differing affinities. This interaction modulates various physiological processes, including pain perception, immune response, and mood regulation, potentially contributing to CBG’s therapeutic benefits. CBG demonstrates potential as a treatment for drug-resistant bacterial infections. Research indicates that CBG exhibits antibacterial properties against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) strains, suggesting its potential as a novel antibiotic agent. In an era marked by increasing antibiotic resistance, CBG’s antibacterial properties offer a promising avenue for combating drug-resistant pathogens. Despite the growing interest in CBG, challenges remain. Regulatory constraints and limited research funding have hindered comprehensive studies into CBG’s therapeutic potential. Additionally, the complex interplay between cannabinoids, known as the entourage effect, suggests that CBG’s efficacy may be influenced by other compounds present in cannabis.
Cannabigerol (CBG) represents a promising frontier in cannabis research and wellness. As scientists dive deeper into its pharmacological properties and therapeutic potential, CBG holds the promise of addressing various health conditions and contributing to the evolving landscape of cannabinoid-based medicine. While challenges persist, the burgeoning interest in CBG underscores its potential significance in shaping the future of cannabis therapeutics and wellness.

